Volkswagen (VW) is considering factory closures in Germany for the first time in its 87-year history, signaling a significant shift in the European auto industry. As German and French automakers struggle to compete in the electric vehicle (EV) market, they are facing disruptive waves of potential factory closures.
The Struggles of European Carmakers
Overcapacity and Declining Competitiveness- Volkswagen

Years of overcapacity and slumping competitiveness have caught up with European manufacturers. Despite efforts to compete with Chinese rivals and Tesla, European automakers like VW, Stellantis, and Renault are struggling. According to Just Auto, these manufacturers were operating over 30 factories at unprofitable levels, including VW’s sprawling home factory in Wolfsburg, Europe’s largest.
The Impact of the Combustion Engine Phase-Out

The European auto industry is uniquely exposed to the decline of the combustion engine. Unlike the U.S., Europe maintained high-cost plants post-financial crisis. Now, with the massive investments needed for electric cars, the loss of cheap Russian energy, and dwindling prospects in China, the region’s auto industry is facing significant challenges.
Financial Strains on Leading Automakers
VW’s Declining Financial Health

Volkswagen has seen its financial health decline, with shares nearing the lows of the 2015 diesel crisis. In July, the group cut its outlook for the year after sales declined in the first half. Margins for VW’s volume brands have narrowed, and profitability for brands like Audi has also worsened.
Stellantis and Renault: Struggling to Keep Up
Stellantis, the parent company of Chrysler, Fiat, and PSA Peugeot Citroen, reported a nearly 50% drop in net profit in the first half of 2024. CEO Carlos Tavares faces pressure amid declining market share and low demand for vehicles like the electric Fiat 500. Renault’s CEO, Luca de Meo, has advocated for a European alliance to pool assets, but time is running out for such strategic initiatives.
The Broader Economic and Political Impact
Germany’s Economic Woes
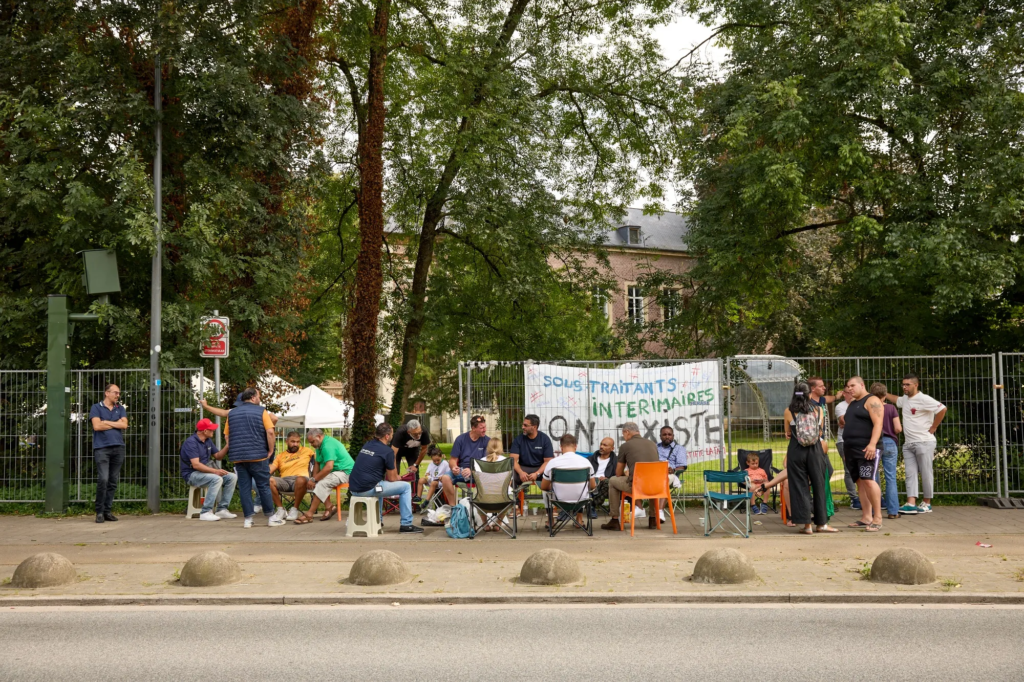
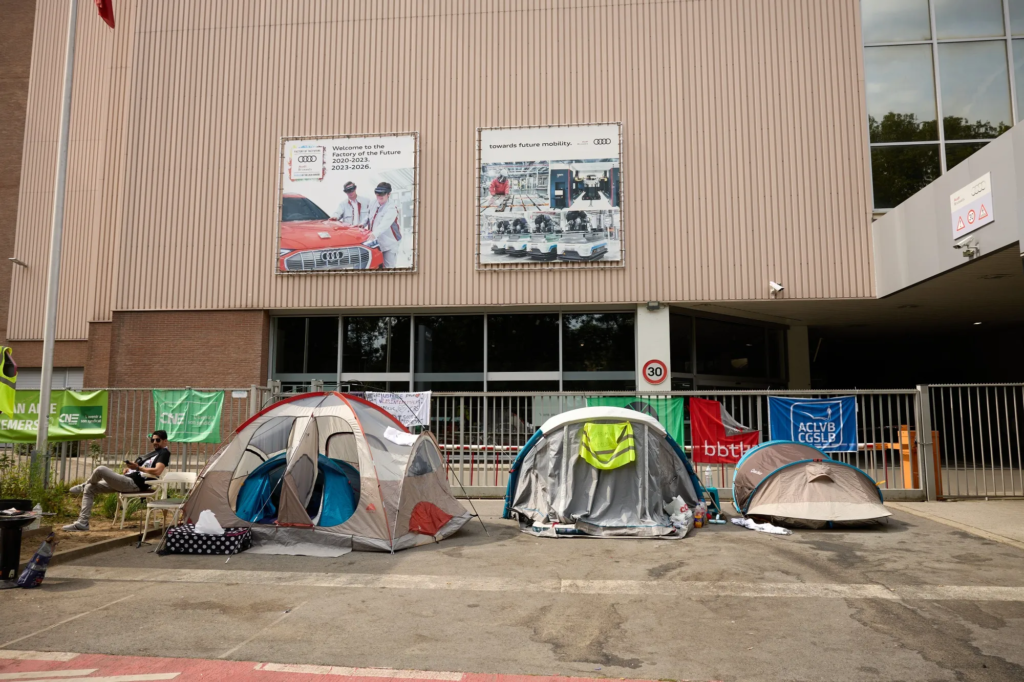
Germany, Europe’s largest economy, is grappling with stagnation, challenges from migration, higher energy costs, and budget austerity. VW’s planned cutbacks add to these woes, threatening jobs and the livelihoods of tens of thousands of workers. The closure of factories, such as the one in Brussels, could have a significant economic impact, with lengthy negotiations needed to soften the blow.
Political Ramifications
State elections in eastern Germany have shown a fragmented political landscape, with the far-right Alternative for Germany party gaining ground. This political shift adds to the uncertainty surrounding VW’s future plans and the broader implications for Germany’s auto industry.
The Future of Europe’s Auto Industry
The Struggle to Compete in the EV Market
Europe’s auto manufacturers entered the electric-car race reluctantly, underestimating the pace of change and new rivals. VW’s cost-cutting steps, though necessary, are the result of missed opportunities in recent years. The EV market’s sluggish uptake has put Europe’s automakers at a disadvantage, with Chinese companies and Tesla gaining ground.
The Human Impact of Factory Closures
For workers like Maurizio Sabatino, who has been with VW for four decades, the threat of factory closures is devastating. The Brussels plant, once a vanguard of VW’s electric-car strategy, is now facing potential closure. The factory’s history mirrors Europe’s rise from post-war rubble to mass affluence, but the transition to electric cars has not gone as planned.
Conclusion: A Critical Juncture for Europe’s Auto Industry
Volkswagen’s potential factory closures in Germany mark a critical juncture for Europe’s auto industry. As the region grapples with declining competitiveness, rising costs, and geopolitical challenges, the future of the industry hangs in the balance. The decisions made in the coming months will have far-reaching implications for the economy, workers, and the global auto market.